Ericsson Telecom Core Components (IMS SBG)
Ericsson Consultant at DEK Technologies Vietnam - Contributing to telecom core components with media control and protocol handling
Project Overview
As Ericsson Consultant at DEK Technologies Vietnam, I contributed to IP Multimedia Subsystem (IMS) Session Border Gateway (SBG) components, a standardized architectural framework for delivering IP multimedia services in telecommunications networks. This mission-critical infrastructure enables voice, video, and data services for millions of users through advanced protocol handling, media control, and fault tolerance mechanisms.
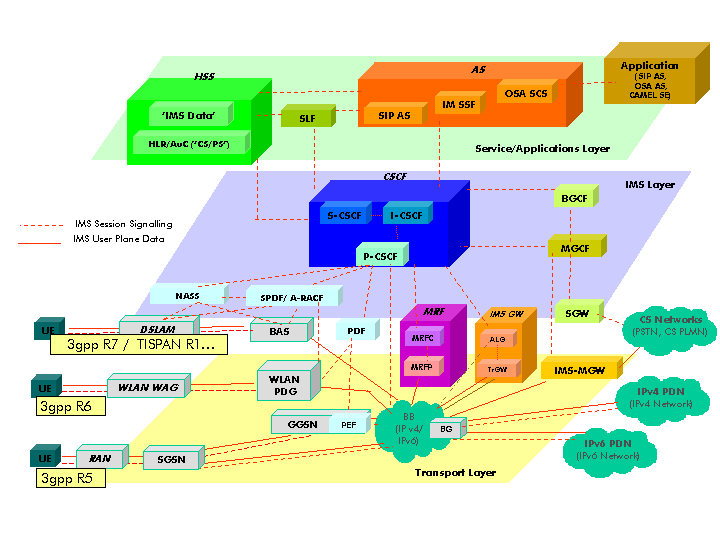
IMS Architecture & Technology
The IP Multimedia Subsystem (IMS) is a standardized architectural framework designed by 3GPP for delivering IP multimedia services over both wireless and wireline networks. It provides a horizontal control layer that isolates access networks from service layers, enabling fixed-mobile convergence (FMC) and supporting services like:
- VoLTE (Voice over LTE): High-quality voice calls over 4G/5G networks
- ViLTE (Video over LTE): Real-time video calling capabilities
- RCS (Rich Communication Services): Advanced messaging and presence features
- Wi-Fi Calling: Seamless voice calls over Wi-Fi networks
- SMS/MMS over IP: Text messaging over packet-switched networks
Session Border Gateway (SBG)
The SBG serves as a critical security and control point in IMS networks, managing:
- Session Control: SIP session establishment, modification, and termination
- Media Control: Real-time media processing for voice/video streams
- Security: Network protection and access control
- Protocol Translation: Seamless communication between different network domains
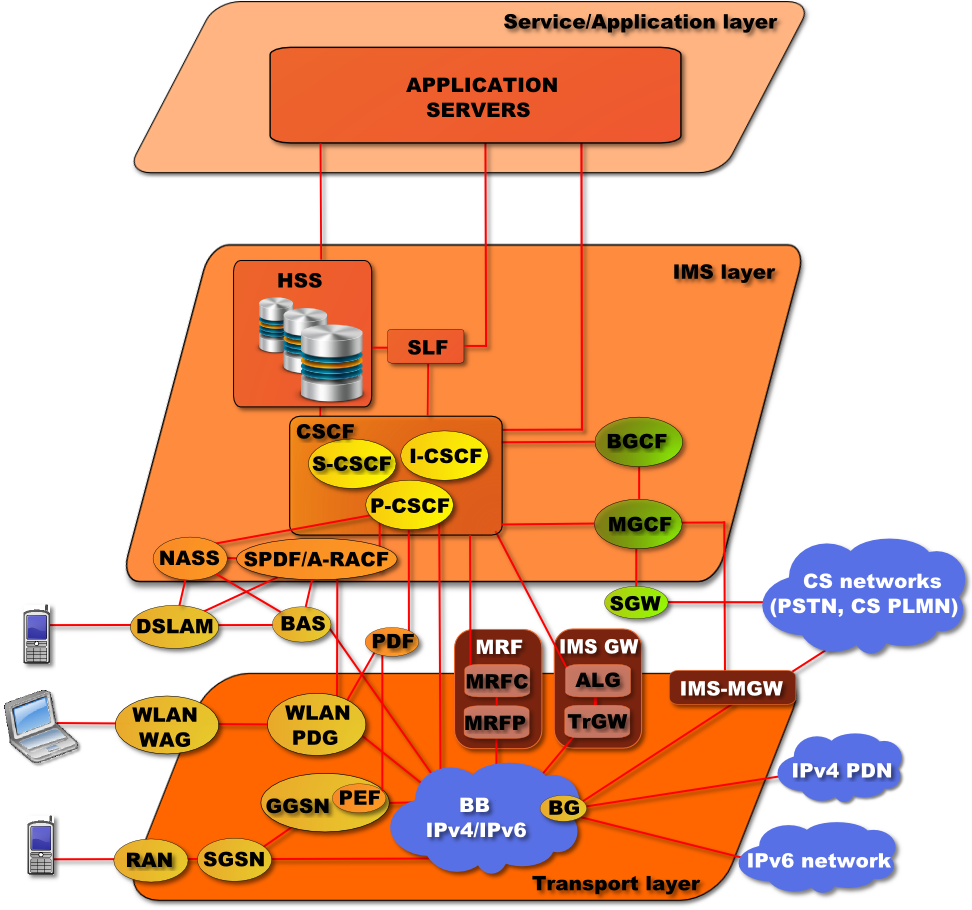
Technical Architecture
Core Components
- IMS SBG: IP Multimedia Subsystem Session Border Gateway components
- Media Control: Real-time media processing and control systems
- Protocol Handling: SIP, Diameter, and Megaco protocol implementations
- Fault Tolerance: Enhanced reliability for telecom core systems
Technology Stack
- Backend: Erlang for concurrent processing and fault tolerance
- Telecom Protocols: SIP, Diameter, Megaco for network communication
- Development Tools: Python for automation and testing
- CI/CD: Jenkins for automated testing and deployment
- Network Analysis: Wireshark for protocol debugging and analysis
Key Features
Telecom Core Development
- Media Control: Real-time media processing and control for voice/video calls
- Protocol Implementation: Robust handling of SIP, Diameter, and Megaco protocols
- Fault Tolerance: Enhanced system reliability for critical telecom operations
- Performance Optimization: Improved throughput and latency for telecom services
Development Excellence
- CI Pipeline Automation: Streamlined development and testing processes
- Cross-disciplinary Testing: Comprehensive testing strategies across multiple domains
- Protocol Analysis: Deep understanding of telecom protocols and standards
- Quality Assurance: Automated testing and validation for telecom systems
Results
Technical Achievements
- Media Control: Improved real-time media processing capabilities
- Protocol Handling: Enhanced reliability of SIP, Diameter, and Megaco protocols
- Fault Tolerance: Strengthened system reliability for critical telecom operations
- Development Efficiency: Automated CI/CD pipelines for faster development cycles
Business Impact
- System Reliability: Enhanced fault tolerance for mission-critical telecom infrastructure
- Development Velocity: Improved development speed through automated testing
- Quality Assurance: Comprehensive testing strategies for telecom core components
- Operational Excellence: Streamlined deployment and monitoring processes
Impact
This work contributed to Ericsson’s telecom core infrastructure, enabling reliable voice and data services for millions of users. The protocol handling improvements and fault tolerance enhancements have influenced best practices for telecom core system development.
Technical Contributions
Protocol Expertise
- SIP Implementation: Robust Session Initiation Protocol handling
- Diameter Support: Authentication, authorization, and accounting protocols
- Megaco Integration: Media Gateway Control Protocol implementation
- Protocol Analysis: Deep debugging and optimization using Wireshark
Development Automation
- Jenkins Integration: Automated CI/CD pipelines for telecom systems
- Testing Strategies: Cross-disciplinary testing approaches for complex systems
- Quality Assurance: Comprehensive validation and testing procedures
- Performance Monitoring: Real-time monitoring and optimization of telecom services
IMS Network Architecture
Core Network Components
- CSCF (Call Session Control Function): Central control element for session management
- HSS (Home Subscriber Server): Central database for user profiles and authentication
- Application Servers: Service logic and application hosting
- Media Servers: Media processing and streaming capabilities
- Breakout Gateways: Interconnection with external networks
Access Network Integration
- 3GPP Networks: UMTS, LTE, 5G mobile networks
- Non-3GPP Networks: Wi-Fi, fixed broadband connections
- PSTN Interconnection: Legacy telephone network integration
- Security Mechanisms: Authentication, authorization, and encryption
References
References and Copyright: This project page incorporates information and images from the IP Multimedia Subsystem Wikipedia article and related Wikimedia Commons resources. The IMS overview diagrams are sourced from Wikimedia Commons and are in the public domain.